TR X 0010:1998/E
DSSSL Library for Japanese Compositions
The Technical Report JIS/TR X 0010:1998 was published as a Type 2 JIS/TR by JSA (Japan Standardization Association) being based on the activities on application technology of DSSSL; Document Style Semantics and Specification Language (JIS X 4153 or ISO/IEC 10179) for Japanese composition environments. Those activities were taken by Application Standards Committee of JBMA (Japan Business Machine Makers' Association) and Electronic Publishing Committee of INSTAC/JSA.
This document is an English version of the JIS/TR X 0010:1998 and includes some editorial corrections and verified DSSSL libraries. The English translation was carried out by the Electronic Publishing Committee of INSTAC/JSA.
This Technical Report provides a DSSSL library that can specify styles for the documents described by SGML; Standard Generalized Markup Language (JIS X 5161 or ISO 8879) or XML; Extensible Markup Language (JIS/TR X 0008 or W3C REC-xml-980210). The library makes it feasible to describe DSSSL specification for ordinary documents without any particular knowledge of DSSSL or Japanese composition rules.
The following standards and technical reports contain provisions that, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of this International Standard. At the time of publication, the editions indicated are valid. All standards are subject to revision, and parties to agreements based on this International Standard are encouraged to investigate the possibility of applying the most recent editions of the standards indicated below.
- JIS X 4153:1998 Document Style Semantics and Specification Language (DSSSL)
- NOTE: Its original is ISO/IEC 10179:1996 Document Style Semantics and Specification Language (DSSSL).
- ISO 8879:1986 Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML)
- NOTE: JIS X 4151:1992 SGML is a Japanese translation of ISO 8879:1986 with some editorial and technical modifications including the specification of ISO 8879/Amendment 1:1988.
- JIS/TR X 0008:1999 Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0
- NOTE: Its original is W3C Recommendation, REC-xml-19980210, Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0.
- JIS X 4051-1995 Line composition rules for Japanese documents
- JIS X 0208-1997 7-bit and 8-bit double byte coded kanji sets for information interchange
- TR X 0003:1996 Glossary of Terms Used in Font Information Processing
- JIS X 4161-1993 Font information interchange: Architecture
- NOTE: Its original is ISO/IEC 9541-1:1991 Font information interchange Part 1: Architecture.
- IEEE Scheme standard, R4RS
For the purposes of this Technical Report, the following definitions apply.
- 3.1 space
- Interval between virtual bodies of adjacent characters or adjacent lines.
- 3.2 line leading
- Displacement between corresponding pointes of adjacent lines.
- 3.3 interline space (or line space)
- Interval between adjacent lines.
-
3.4 character writing direction
- Direction of characters composing in lines. Most of Japanese texts employ the vertival or horizontal in their composition direction.
-
3.5 group-ruby
- Ruby scheme aligning ruby characters along all the objects (character sequence).
- 3.6 emphasizing mark
- A symbol located on a side (right in vertical composition or above in horizontal composition) of a character sequence to be emphasized.
- 3.7 edge
-
One of the three sides of page that are not binded. The three sides are top edge, bottom edge and front edge.
- 3.8 indentation
- Line head shifting along its character progression direction.
- 3.9 number of characters on a line
- The number of characters which are included in a line.
- 3.10 character of numbering
- Head character of each ordered list item, indicating the order of the list item.
- 3.11 cell
- The basic unit in a table composition.
- 3.12 superscript/subscript (or superior/inferior)
- Small characters allocated on a side (just right-top or right-bottom respectively) of an object chacater.
- 3.13 single page
- A separated page. It is employed specifically descriminating the page from a facing page.
- 3.14 column
- A separated composition area within a page.
- 3.15 column space
- Interval between adjacent column.
- 3.16 bottom edge
- Bottom side on a page layout.
- 3.17 top edge
- Top side on a page layout.
- 3.18 DSSSL library
- A set of DSSSL specifications.
- 3.19 clock numerical
- A Roman numerical chacater designed for a clock face.
- 3.20 2-chcracter ruby
- Ruby with half a virtual body size (measured in the character progression direction) of an object character.
- 3.21 gutter
- Binding area of a book.
- 3.22 page number
- The number indicating a page sequence.
- 3.23 head line
- Title of a book, chapter or section allocated on margin areas of a page.
- 3.24 image area
- The major area where main texts are composed.
- 3.25 writing mode
- Character progression direction on a line. [The direction to escapement point from position point on a glyph coordinate system (see JIS X 4161).] In Japanese composition, the writing mode is LEFT-TO-RIGHT or TOP-TO-BOTTOM.
- 3.26 table caption
- Title or other description of a table. It is sometime referred to table title or table heading.
- 3.27 additional character
- Characters just before and/or after ordering characters.
- 3.28 solid matter (or solid)
- A composition without any margin between adjacent characters or lines.
- 3.29 strike-through (or strike-out)
- A line over characters indicating deletion of them.
- 3.30 facing page
- Two-page (left and right page) spread in a book.
- 3.31 character size
- The size of a virtual body.
- 3.32 mono-ruby
- Ruby scheme aligning ruby characters with respect to each object character.
- 3.33 ruby
- A small character sequence located on a side of an object character sequence indicating the pronounciation, meaning, etc. of the object.
This clause defines formatting objects and properties used in this DSSSL Library.
The following paper sizes are specified:
- A-size: A6, A5, A4
- B-size: B6, B5
The selection of "Single Page" or "Facing Page" is permitted. The double of Paper size is permitted in case of "Facing Page".
NOTE: "Facing Page of A4" = A3.
"Portrait placement" and "Landscape placement" are specified.
It defaults to "Portrait placement".
The following three derived units are defined:
- mm
- Point (1point = 0.3514mm)
- Q (1Q = 0.25mm)
The relationship between Q and Point is required to refer to Table 4.1.
Table 4.1 Relationship of Q and Point
| Q | Point | Q | Point |
| 7 | 5 | 15 | 10.5 |
| 8 | 5.5 | 16 | 11 |
| 9 | 6 | 18 | 12 |
| 10 | 7 | 20 | 14 |
| 11 | 7.5 | 21 | 15 |
| 12 | 8 | 24 | 16 |
| 13 | 9 | 26 | 18.5 |
| 14 | 10 | 28 | 20 |
The following items are defined.
- size of image area
- margin
- basic composition styles
Basic composition styles are defined by following formatting objects:
- vertical composition or horizontal composition
- size of character
- number of characters in a line
- number of lines in a column
- interline space
- column space
The methods to specify basic composition styles are following two types:
- To specify by the numerical value for each formatting object of image area definition.
- To use value of Table 4.5.
NOTE: The methods of calculation for the image area and margin are following two
types:
- layout driven: paper size - margin = image area
- content driven: paper size - image area = margin
In Japanese composition content driven are used usually. Those methods define the image area first then margin.
4.5.1 Specification of the position for image area
Specifications of the position for image area are defined by the following types:
- The image area is placed center of the rectangle surrounding the
margin of top edge, bottom edge, front edge and gutter (default).
- Image area is specified by the ratio of head edge, tail edge, front edge and gutter.
- Image area is specified by the absolute value.
NOTE:When the size of image area is not specified, the vertical and horizontal size of image area is made 0.8 times of paper size.
4.5.2 Model of basic composition styles
The models of basic composition styles for each paper size are defined by the following Table 4.2 to Table 4.8:
Table 4.2 B6-size Vertical placement (Point system)
| Vertical/Horizontal composition |
Size of character | Number of characters on a line |
Number of lines on a column |
Line leading |
Number of Columns |
Column space |
| Vertical |
9 point |
43 |
14 |
18 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
9 point |
43 |
15 |
18 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
9 point |
43 |
16 |
17 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
9 point |
44 |
17 |
16 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
8 point |
50 |
18 |
15 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
8 point |
50 |
19 |
14 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
8 point |
25 |
20 |
14 point |
2 |
2 characters |
| Vertical |
8 point |
26 |
20 |
14 point |
2 |
2 characters |
| Horizontal |
9 point |
30 |
23 |
17 point |
1 |
. |
| Horizontal |
8 point |
33 |
25 |
16 point |
1 |
. |
| Horizontal |
8 point |
33 |
27 |
15 point |
1 |
. |
| Horizontal |
8 point |
34 |
27 |
15 point |
1 |
. |
Table 4.3 B5-size Vertical placement (Point system)
| Vertical/Horizontal composition |
Size of character |
Number of characters on a line |
Number of lines on a column |
Line leading |
Number of Columns |
Column space |
| Vertical |
8 point |
24 |
31 |
13 point |
1 |
. |
| Horizontal |
9 point |
43 |
32 |
18 point |
1 |
. |
| Horizontal |
9 point |
23 |
44 |
14 point |
2 |
2 characters |
| Horizontal |
9 point |
22 |
41 |
15 point |
2 |
2 characters |
| Horizontal |
8 point |
25 |
51 |
12 point |
2 |
2 characters |
Table 4.4 B5-size Vertical placement (Q system)
| Vertical/Horizontal composition |
Size of character |
Number of characters on a line |
Number of lines on a column |
Line leading |
Number of Columns |
Column space |
| Horizontal |
13 Q |
42 |
31 |
26 Q |
1 |
. |
| Horizontal |
13 Q |
22 |
43 |
20 Q |
2 |
2 characters |
| Horizontal |
13 Q |
21 |
39 |
22 Q |
2 |
2 characters |
| Horizontal |
12 Q |
23 |
48 |
18 Q |
2 |
2 characters |
Table 4.5 A6-size Vertical placement (Point system)
| Vertical/Horizontal composition |
Size of character |
Number of characters on a line |
Number of lines on a column |
Line leading |
Number of Columns |
Column space |
| Vertical |
8 point |
41 |
13 |
17 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
8 point |
41 |
14 |
16 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
8 point |
42 |
15 |
15 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
8 point |
42 |
13 |
16 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
8 point |
42 |
14 |
16 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
8 point |
43 |
15 |
15 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
8 point |
43 |
16 |
14 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
8 point |
43 |
18 |
13 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
8 point |
43 |
19 |
13 point |
1 |
. |
Table 4.6 A5-size Vertical placement (Point system)
| Vertical/Horizontal composition |
Size of character |
Number of characters on a line |
Number of lines on a column |
Line leading |
Number of Columns |
Column space |
| Vertical |
9 point |
51 |
16 |
18 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
9 point |
52 |
16 |
18 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
9 point |
52 |
17 |
18 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
9 point |
52 |
18 |
17 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
9 point |
52 |
19 |
17 point |
1 |
. |
| Vertical |
9 point |
25 |
20 |
15 point |
2 |
2 characters |
| Vertical |
8 point |
30 |
24 |
13 point |
2 |
2 characters |
| Vertical |
8 point |
29 |
23 |
14 point |
2 |
2 characters |
| Horizontal |
9 point |
35 |
26 |
18 point |
1 |
. |
| Horizontal |
9 point |
35 |
28 |
17 point |
1 |
. |
| Horizontal |
9 point |
35 |
30 |
16 point |
1 |
. |
| Horizontal |
8 point |
40 |
30 |
16 point |
1 |
. |
| Horizontal |
8 point |
38 |
33 |
14 point |
1 |
. |
Table 4.7 A5-size Vertical placement (Q system)
| Vertical/Horizontal composition |
Size of character |
Number of charactesr on a line |
Number of lines on a column |
Line leading |
Number of Columns |
Column space |
Horizontal |
13 Q |
34 |
27 |
25 Q |
1 |
. |
| Horizontal |
13 Q |
34 |
29 |
23 Q |
1 |
. |
| Horizontal |
12 Q |
37 |
28 |
24 Q |
1 |
. |
| Horizontal |
12 Q |
36 |
31 |
21 Q |
1 |
. |
Table 4.8 A4-size Vertical placement (Q system)
| Vertical/Horizontal composition |
Size of character |
Number of characters on a line |
Number of lines on a column |
Line leading |
Number of Columns |
Column space |
Horizontal |
13 Q |
51 |
41 |
24 Q |
1 |
. |
| Horizontal |
14 Q |
48 |
39 |
25 Q |
1 |
. |
| Horizontal |
14 Q |
24 |
42 |
23 Q |
2 |
2 characters |
| Horizontal |
14 Q |
16 |
42 |
23 Q |
3 |
2 characters |
The typeface designation is required to designate a generic font family name in Japanese such as "mincho", "gothic". In this TR the typeface designation is not permitted to use any proper typeface name. This TR is required to use "a generic font family name, weight" and "a western language font family name, weight" in font family name designations.
This technical report (JIS/TR) is not provided for posture and the classification between KANJI and KANA.
Character size is to use "Point" or "Q" as a unit of the character size.
Note: This technical report (JIS/TR) is not provided for "the horizontal condensed", "the vertical condensed" and "slant".
4.8.1 Number of headlines
Number of headlines is required to choose one from the following cases:
- an unused headline
- one headline
4.8.2 Position of headline
Position of headline is required to choose one from the following cases:
- near edge in the top edge on an odd-page
- near edge in the top edge on both an odd-page and an even-page
- near edge in the tail edge on an odd-page
- near edge in the tail edge on both an odd-page and an even-page
- center in the top edge (in the case of the horizontal composition)
The headline must be composed the horizontal composition in every case. If the headline and the page number are the same position, this technical report (JIS/TR) requires arranging a little to the edge as a position of the page number, and the headline must be arranged inside from the page number. And this technical report (JIS/TR) requires leaving full space or 1.5 times space between the headline and
the page number.
The rule of division of words at the headline shall be referred to 4.15.
4.8.3 Contents of headline
If the contents of headline differ in both an odd-page and an even-page, this technical report (JIS/TR) requires choosing one from the following cases as style of headline.
- near edge in the top edge on both an odd-page and an even-page
- near edge in the tail edge on both an odd-page and an even-page
- center in the top edge (in the case of the horizontal composition)
If the headline consists of the contents of upper structure in the logical structure, the headline must be arranged opposite the page to begin the text. And the headline on the opposite page must be consisted of the contents of lower structure. However, the headline must not be arranged on the page to begin the text.
Style of the page number is provided for style of following two cases:
- near edge in the top edge, Arabic numerals
- near edge in the tail edge, Arabic numerals
The character size of the page number is to use the same size of the text or one grade below. The distance between headline and image area is required to designate the character size of the text or one grade up.
Style of note is provided for the following four types (The inlinenote shall be referred to 4.11.):
- sidenote (in the case of the horizontal composition)
- footnote (in the case of the horizontal composition)
- headnote (in the case of the vertical composition)
- interlinenote
This technical report (JIS/TR) is regarded the endnote as the text.
This technical report (JIS/TR) is provided for designation of the following cases a. to d. as style of note.
- Characters of reference mark (include "none of reference mark") and style
This technical report (JIS/TR) requires to use characters of "", "ő", "ö", "", "a", "", "Arabic
numerals", "KANJI numerals" and "alphabet" as reference mark. And this technical report (JIS/TR) requires to use "1), 2),cc" as reference mark at default of designation.
NOTE:Some examples of reference mark are as follows:
| | | |
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 1) | 2) | 3) |
| ęA | ńA | OA |
| (a) | (b) | (c) |
- Positions of reference mark
- Put a line space at the head of words and phrases for note.
- Put a line space at the end of words and phrases for note.
- Continue in inline at the end of words and phrases for note.
- Character size of reference mark
- Types of note (sidenote, footnote, headnote)
Note 1: Types of note in the Japanese composition are following Note 2 to Note 6 cases.
Note 2: Interlinenote
This note is composed in a line space beside words and phrases for note. This note is composed in upper line space in the case of the horizontal composition, and in right line space in the case of the vertical composition. The Fig.4.1 means an example in the case of the horizontal composition.
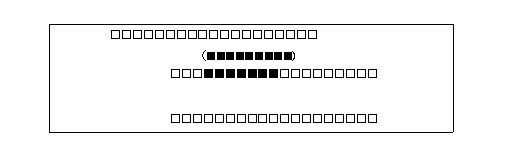
Fig.4.1 An example of interlinenote in the case of horizontal composition.
Note 3: Sidenote
This note is composed in a note area at a little to the edge in the case of the horizontal composition. See Fig.4.2.
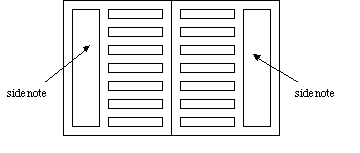
Fig.4.2 Sidenote
Note 4: Headnote
This note is composed in a note area at a little to the top edge in the case of the vertical composition. See Fig.4.3.
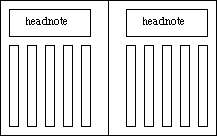
Fig.4.3 Headnote
Note 5: Footnote
This note is composed in a note area at a little to the tail edge. The Fig.4.4 means an example in the case of the vertical composition.
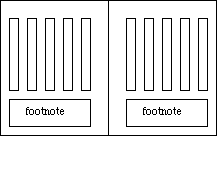
Fig.4.4 An example of footnote in the case of vertical composition
Note 6: Endnote
The note is composed at the end of division in the text, such as volume, section, part and paragraph, or at the end of a book.
In this rule, the only Inline note of two lines is provided. The inlinenote is managed within same line. We refer this kind of inline in 4.25 for details. Without any specification, to decorate with Inlinenote parenthesis. The size of parenthesis defined as the same size of the body characters size. A default size for Inlinenote characters is defined as 50% of body characters size, but changeable. The line space between the Inlinenote lines is 0 as a default, but changeable. This rule of line compositions image for Inlinenote lines is totally depended on the format.
An emphasizing mark can be used as a unit of character, word or paragraph. The emphasizing mark can put on the top (horizontal composition) or the right (vertical composition) of the character (parent character) as a principle rule. The rule of decorating Emphasizing mark is defined by the "mark style". To decorate Emphasizing mark can be chosen from "each character" or "equal to the group of characters". The default style of the emphsizing mark is defined as "each character" and, "without style". When you use an "equal to the group of characters"Cthe beginning to end point position of the emphasing mark is defined by the format.
This is provided for Superscript and Subscript. In vertical composition, it is changed in each of the positions of Superscript as the right under the character (parent character) of the object and Subscript as the left under the character (parent character) of the object. A size of Superscript and Subscript is half of the parent character. Both of "superscript" and "subscript" can be decorated to one parent character at same time. However, of course this rule depends on the format. The position for a parent character depends on the format, but it should not go over the body of parent character. Even if it go over the body of parent character, it should be included as the subject of the chapter 4.25 "Inline".
A line length of words defined as a result of the multification of the number of characters and the characters size. The amount of character space should be expressed by the following next equation by the character size, the number of line length of words and the number of characters.
amount of character space
= ((all length) - (character size)) / (number of characters space)
= ((character size) * (number of line length of words) -1) / (number of characters) -1
NOTE:The line length of words is used as the designation to complete the string for the number of characters that to be different in the fixed length in case of composing string on the cell of the table and so on. An example is shown Fig. 4.5.
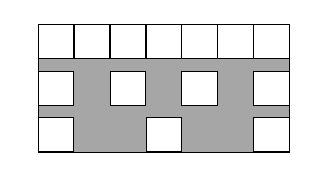
Fig.4.5 Example of Line length of words
We prescribe about typical division of words for a head line. This rule is used even if it is established as standard of division of words for a head line.
Table 4.9 The amount of space of the character space by number of head line characters
| Size B5 Horizontal composition | Size B5 Vertical composition |
| Number of characters | Space | Number of characters | Space |
| 2 | Treble | 2 | Double |
| 3 | Full and Half | 3 | Full and Quater |
| 4 | Full | 4 | Half and Quater |
| 5 | Half | 5 | One Third |
| 6 | Quater | 6 | 1 point |
| 7 | 1 point | over 7 | No |
| over 8 | No | . | . |
NOTE:When lines for few characters such as head line or head line etc. is composed to put the space between the letters corresponding to the number of characters. An example is shown Fig. 4.6 .
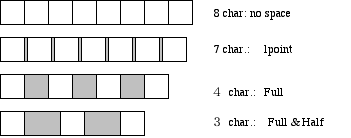
Fig.4.6 example for Division of words
Following two class:
- numbering ordered chapter
- numbering un-ordered chapter
4.16.1 Numbering ordered chapter
- Specify following any character class:
English capital letter, KANJI numeric, Arabic numeric, Roman big English capital letter, clock numeric
- Decorations for numbering specified following type class:
- no decoration character
- "ć" in front, "Ň", "Í", "ß", " etc. followed
- chapter followed
- period followed@(the period of Japanese or English)
- punctuation followed KANJI numeric
- Font of numbering ordered character
- chapter ć1Í, 1.1, 1.1.1 for unspecied
4.16.2 Numbering un-ordered chapter
- Decorations for numbering specified following type class:
Note 1:As for the image, it means the figure and so on added as the tip part in a next example to show in the head line.
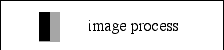
Note 2:As for a indent, we will treat in the 4.19.
Note 3:Making chapters of the manual kind is faced toward the outside of the object
Note 4:No Numbering is specified when there is "Preface" with no section number and so on before the first chapter.
following two class:
- ordered list
- un-ordered list
4.17.1 ordered list
- specify following any character class:
English capital letter, English small letter, KANJI numeric, Arabic numeric, Roman big numeric, Roman small numeric, clock numeric, HIRAGANA, KATAKANA
- specify for ordered character
- un-ordered character
- encircle ordered mark (English capital letter, English small letter, Arabic numeric, HIRAGANA, KATAKANA)
NOTE:
@,
A etc.
- parenthesis enclosed
NOTE:(1),(2) etc.
- parenthesis followed
NOTE:1),2) etc.
- period followed
NOTE:1. , 2. etc.
- Japanese comma followed
NOTE:ęA, ńA etc.
- order of KANA (HIRAGANA and KATAKANA)
- GOJYUON order (a, i, u, e, o, c)
- IROHA order (i, ro, ha, ni, ho, c)
- typeface of ordered mark
- (1), A. , a) for un-specify
4.17.2 character for un-ordered list
- mark
E (dot), , , KANJI numeric of 1 following Japanese comma (ęA), name of character (ruled by standard of coded character)
- typeface of KANJI numeric
4.17.3 indentation of list
- indentation space on a first line of list
indentation of 1 character, indentation of 2 characters
- indentation space on a second line of list
non- indentation , indentation of 1 character, indentation of 2 characters, indentation of 3 characters
4.18.1 character size relationship of table and table caption
- in case of typeface GOTHIC
same size
- in case of typeface MINCHO
1 point smaller than table, or 1Q (= 0.25mm) smaller than table line space of tablenote is half space of tablenote font size
4.18.2 space between table and image area,text
- between table and image area
1mm
- between table and text
1.5 times, character of text
In this composition, 2 specify models are offered following 4.19.1 and 4.19.2.
4.19.1 index of heading font size
- large heading
select in 24`32Q (1Q=0.25mm) or 16`22point
- middle heading
select in 18`20Q (1Q=0.25mm) or 12`14point
- small heading
select in 14`16Q (1Q=0.25mm) or 10`11point
NOTE:These heading font size are in case of 8`9point (12`13Q) text font size. We do not make libraly in this index,because these fontsize are varied by typeface and weight.
4.19.2 heading composition
Font size unit is point system. Using Q system, the relationship table refered to 4.3 Table 4.1 is applied.
Following samples are about "A5 size, vertical composition, text font size 9 point" and "A5/B5 size, horizontal composition, text font size 9/8 point".
- A5 size, vertical composition, text font size 9 point
- sample of one heading
| large heading (14 point) | text font size 9 point~4 indentation | center of 4 lines
|
| middle heading (12 point) | text font size 9 point~6 indentation | center of 3 lines
|
| small heading (10 point) | text font size 9 point~7 indentation | center of 2 lines
|
- sample of 3 headings; large, middle, small
| 1 line space
|
| large heading (14 point) | text font size 9 point~4 indentation | center of 3 lines
|
| middle heading (12 point) | text font size 9 point~6 indentation | center of 2 lines
|
| small heading (10 point) | text font size 9 point~7 indentation | center of 2 lines
|
| 8 lines space in total, including first 1 line space
|
- sample of 2 headings; large, middle
| 1 line space
|
| large heading (14 point) | text font size 9 point~4 indentation | center of 2 lines
|
| middle heading (12 point) | text font size 9 point~6 indentation | center of 3 lines
|
| 6 lines space in total, including first 1 line space
|
- sample of 2 headings; large, small
| 1 line space
|
| large heading (14 point) | text font size 9 point~4 indentation | center of 3 lines
|
| small heading (10 point) | text font size 9 point~7 indentation | center of 2 lines
|
| 6 lines space in total, including first 1 line space
|
- sample of 2 headings; middle, small
| 1 line space
|
| middle heading (12 point) | text font size 9 point~6 indentation | center of 2 line
|
| small heading (10 point) | text font size 9 point~7 indentation | center of 2 lines
|
| 5 lines space in total, including first 1 line space
|
- sample of no heading
- A5/B5 size, horizontal composition, text font size 9/8 point
- sample of one heading
| large heading (14 point) | center of text line width | center of 4 lines
|
| middle heading (12 point) | center of text line width | center of 3 lines
|
| small heading (10 point) | center of text line width or text font size 9 point~1 indentation | center of 2 lines
|
- sample of 3 headings; large, middle, smallcccpage break
| 1 line space
|
| large heading (14 point) | center of text line width | center of 3 lines
|
| middle heading (12 point) | center of text line width | center of 2 lines
|
| 8 lines space in total, including first 1 line space
|
- sample of 2 headings; large, middlecccpage break
| 1 line space
|
| large heading (14 point) | center of text line width | center of 2 lines
|
| middle heading (12 point) | center of text line width | center of 3 lines
|
| 6 lines space in total, including first 1 line space
|
- sample of 2 headings; large, smallcccpage break
| 1 line space
|
| large heading (14 point) | center of text line width | center of 3 lines
|
| small heading (10 point) | center of text line width or text font size 9 point~1 indentation | center of 2 lines
|
| 6 lines space in total, including first 1 line space
|
- sample of 2 headings; middle, smallcccpage break, page non-break
| 1 line space
|
| middle heading (12 point) | center of text line width | center of 2 lines
|
| small heading (10 point) | center of text line width or text font size 9 point~1 indentation | center of 2 lines
|
| 5 lines space in total, including first 1 line space
|
The ruby style standerd designations are below.
- Script length is limited within two ruby charactors.
- Both vertical composition and horizontal composition must be ruby center.
- Permit both mono-ruby and group-ruby.
- In case of mono-ruby, extend the ruby line length in both vertical and horizontal direction symmetrically in case of increasing the number of ruby script. Moreover, ruby scripts must be located in solid matter.
- Ruby script cannot be used over KANJI which located in next to the ruby object script.
- Only one ruby script can be used over KANA which located in next to the ruby object script.
- In case of group ruby, the relationship between ruby and quantity of space must be same as Figure 4.7 (additionally, if ruby line length is longer than ruby object script, ruby line must be solid matter).
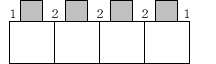
Figure 4.7 Spacing between ruby character in grouped ruby
- The management of beginning and the end of line must be in ruby object script reference.
The paragraph indentation style designate in beginning of the paragraph must be chosen from either "non indentation" or "one indentation".
The table style does not have to be librarize. The rule of script style from 4.14 should be used.
The score must be three styles below. In case of vertical composition, underlineCupperline is changed to leftlineCrightline. The instances of the score are below.
| underline: | 
|
| upperline: | 
|
| strike-out: | 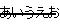
|
NOTE:underlineCupperline(leftlineCrightline) are sometimes just called sideline. The types of the line is shown in 4.24.
The patterns of rule must be only those which shown in diagram 4.10. Those thickness of lines is just an example, and the actual line and line space depend on formatters.
Diagram 4.10 Patterns of rule
| Pattern | Rule image
|
| thin rule | 
|
| medium rule | 
|
| thick rule | 
|
| dotted rule | 
|
| dash rule | 
|
| one dotted dash rule | 
|
| two dotted dash rule | 
|
| parallel rule | 
|
| shaded rule | 
|
Frequently, the element which changes the wideness of the paragraph can be added in script line which compose one paragraph. In this section, style specification elements are the elements which change the wideness of the paragraph.
- Reference mark of note
- Inlinenote
- Emphasizing mark
- Superscript/subscript(superior/inferior)
- Ruby
- Score
When using these elements and compose a sentence, the order of the composition must be based on 4.25.1 and 4.25.2.
4.25.1 The paragraph wideness
In principle, the wideness of paragraph which contain style specification elements must be same numeric value as the paragraph which does not contain any of those elements.
4.25.2 The paragraph location
The locatoin of paragraph which contain style specification elements must be located same location as the case when the paragraph does not contain any of these elements.
The DSSSL library is a framework that enables to specify Document Style and Specification Language (DSSSL) descriptions easily for Japanese structured documents.
DSSSL is the way to specify structure translation and formatting process of SGML documents.
In DSSSL specification, user can specify detailed and precise descriptions for formatting process of SGML documents. However, the specifications are not easy to write for an average user. So, we consider simplify DSSSL specifications by using DSSSL library.
In DSSSL library framework, user can make detailed descriptions from simple descriptions by scheme translation program. DSSSL library includes DSSSL descriptions of standard formatting specifications and standard page model specifications that user can refer. To make detailed descriptions from simple descriptions, translation program needs rules of standard Japanese typesetting rules, formatting specification and there parameters.
NOTE:the library does not support followings:
DSSSL script can be written highly system independent, detailed and generic description for DSSSL users. And they should need following knowledge to use DSSSL:
- DSSSL formatting process
- compositions
- DSSSL Flow Object Class for composition elements
- SGML
- Grove (data structure inner DSSSL)
- Scheme (expression language for DSSSL syntax)
- SDQL (query operations)
We want to provide the way that beginner can use easily DSSSL processing system without lossing flexibility of the DSSSL specification ability.
We should provide one DSSSL library for each following levels of user's needs.
- level 0
User can use predefined styles. : for example, when people want to output HTML document in predefined style.
- level 1
User can understand formatting parameters in DSSSL and custamize style.
- level 2
User can specify DSSSL specification for DTD using library.
- level 3
User can create library or enhance library for re-use.
Library framework provide a high level description of DSSSL language. User can flexibly change parameters of library or add a low level descriptions.
This technical report (JIS/TR) mainly gives level 1 library.
The processing flow of DSSSL library is shown in fig5.1
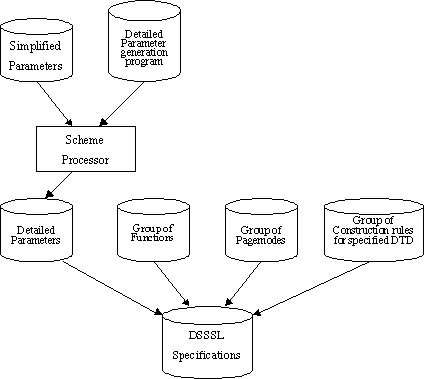
fig.5.1 the processing flow of DSSSL library
DSSSL library consists of 4 part:
- detailed parameter generator
- function library
- page model library
- DTD rule library
5.2.1 simplified parameter
DSSSL library needs to support generating detailed parameters from simple user request. To achive this, the detailed parameter generator generate default parameters for standard Japanese composition method if not specified in simple parameters. For example ruby font size is ordinary half of base font size. In Japanese composition method, image area size is specified in multiple of base font size.
If user can not satisfied default parameters, user can give detailed parameters in simplified specification description. detailed parameter generater get these parameters and generate detailed parameters.
5.2.2 Detailed Parameter Generator
Detailed parameter generator generate detailed parameters from simplified parameters.
Using composition model described in chapter 4, program generate parameters used in the function library and the page model library. Program is shown in Annex A.
5.2.3 Function Library
We prepare functions used in DSSSL specifications to describe composition elements. These functions are DSSSL flow object generating functions and its support functions used in construction rules in DSSSL specifications. The detailed parameters are refered by these functions. These are shown in Annex B.
5.2.4 Page Model Library
Page model library provide page model descriptions in DSSSL style language. These use detailed parameter to define styles of page. These are shown in Annex C.
5.2.5 DTD Rule Library
DTD rule library gives concrete DSSSL specifications to specific DTD, uses detailed parameters, function library and page model library, and specifies construction rules of each DTD tag. In this version, DTD rule library provide construction rules to each HTML 3.2 tags. Thse are shown in Annex D.
Simplified parameters are source of detailed parameters, given in association list form to detail parameter generater. Parameters list is below.
Unit of length is [mm] if no unit is specified. User can give unit like 9pt [ 1pt = 0.3514mm, Q = 0.25mm ].
-
*paper-name*
-
paper size description (string, default "a4")
-
*paper-direction*
-
paper directionistring: "portrait"/"landscape")(default "portrait")
-
*writing-direction*
-
writing direction (string: "horizontal"/"vertical")(default "horizontal")
-
*paper-width*
-
paper width ([mm] : *paper-name* dependent)
-
*paper-height*
-
paper length ([mm]: *paper-name* dependent)
-
*column-number*
-
number of columns (number)(default 1)
-
*base-font-size*
-
base font size ([mm])
-
*standard-composition*
-
image area specification (string)
-
*page-spec*
-
Basic page specification list (list of body font size, number of character in line, lines in page, line width, column number, space between column)
-
*page-region-width*
-
image area width ([mm])
-
*page-region-height*
-
image area height ([mm])
-
*area-x-ratio*
-
area vertial ratio of image area (0.0`1.0)(default 0.5)
-
*area-y-ratio*
-
area holizontal ratio of image area (0.0`1.0)(default 0.5)
-
*page-region-x-offset*
-
page region holizontal offset
-
*page-region-y-offset*
-
page region vertical offset
-
*font-table*
-
font information table of heading font (list)
-
*rubi-font-size-factor*
-
ruby font size ratio from base font size (0.0`1.0)(default 0.5)
-
*subscript-font-size-factor*
-
subscript font size ratio from base font size (0.0`1.0)(default 0.3)
-
*superscript-font-size-factor*
-
superscript font size ratio from base font size (0.0`1.0)(default 0.3)
-
*base-font-family*
-
base font family specification (default "mincho-light, sans-medium")
-
*jisage-factor*
-
number of characters of indentation of paragraph (default 1)
-
*indent-factor*
-
number of characters of indentation of ordered list (default 2)
-
*has-header-nonburu*
-
exsistance of page number at top edge (#t/#f)(default #t)
-
*has-header-hasira*
-
existance of headline at top edge (#t/#f)(default #t)
-
*has-footer-nonburu*
-
existance of page number at tail edge (#t/#f)(default #f)
-
*has-footer-hasira*
-
existance of headline at tail edge (#t/#f)(default #f)
-
*hasira-rect*
-
headline string of rect page (string)
-
*hasira-verso*
-
headline string of varso page (string)
-
*footnote-number-desc*
-
number description of foot note (string)
-
*enum-number-desc*
-
top character of ordered list (string)
-
*title-number-desc*
-
heading number description (string)
end of main